Maternal Mortality in the U.S. Preventable Deaths Rise
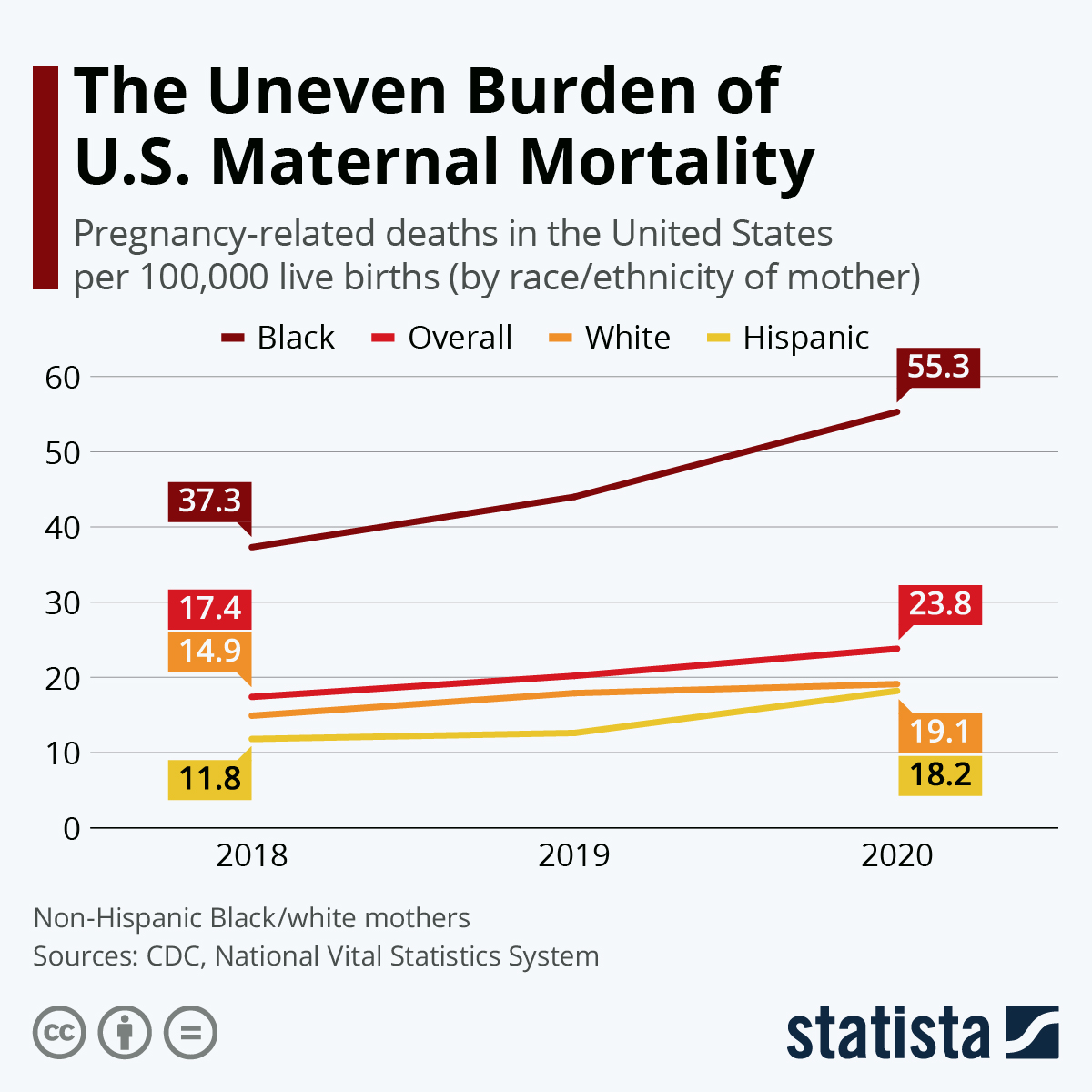
Maternal mortality in the U.S. is a pressing public health crisis that continues to escalate. This nation, while a leader among high-income countries, has an alarmingly high rate of pregnancy-related deaths, with a staggering statement that over 80 percent of these fatalities are preventable. Recent studies reveal a troubling trend, as maternal mortality rates rose sharply between 2018 and 2022, underpinned by significant racial disparities and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal health care. The findings highlight a critical need for enhanced prenatal and postpartum care, especially to bridge the widening gap caused by racial inequities in maternal health. Addressing these issues is essential to achieving equitable health outcomes for all mothers, ensuring that no preventable maternal death occurs during or after pregnancy.
In the United States, the issue of maternal mortality has reached concerning levels, illustrating the urgent need for reform in pregnancy and maternity care. Terms such as “pregnancy-related fatalities” or “deaths during and post-pregnancy” capture the severity of this health crisis, which disproportionately affects marginalized communities. The rising incidence of preventable maternal deaths underscores the deficiencies in our current healthcare framework, pointing to a clear mandate for improved support systems during both prenatal and postpartum periods. Moreover, the stark racial disparities in maternal health outcomes reveal systemic inequities that perpetuate poor health among specific demographic groups. A comprehensive understanding and response to these challenges are vital for transforming maternal health care across the nation.
Understanding Maternal Mortality in the U.S.
Maternal mortality in the U.S. is a concerning public health issue, especially as data reveals a rising trend in pregnancy-related deaths. Unlike many other high-income countries, the U.S. leads in maternal mortality rates, with significant complications often being preventable. Research indicates that over 80 percent of these deaths could be avoided through better access to healthcare and targeted interventions during prenatal and postpartum care. The stark differences in care quality across states highlight the need for a more cohesive approach to maternal health.
The reasons for this high maternal mortality are multifaceted, encompassing systemic healthcare flaws, racial disparities, and a lack of adequate support for mothers during the critical postpartum phase. Discrimination in healthcare systems means that women of color, particularly American Indian and Black women, suffer disproportionately from complications related to pregnancy. To combat these issues, it is vital to examine how to improve care models and policy implementations, ensuring that every mother has access to comprehensive maternal health services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
In the U.S., the leading causes of maternal mortality include cardiovascular disease, hemorrhage, and other pregnancy-related complications. Chronic medical conditions, such as hypertension, have increasingly contributed to these deaths, highlighting the need for better maternal health care throughout pregnancy and the postpartum period.
How do preventable maternal deaths in the U.S. compare to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has one of the highest rates of preventable maternal deaths among high-income countries, with over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths deemed preventable. This stark contrast emphasizes the urgent need for improved maternity care and healthcare access.
What are the racial disparities in maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Significant racial disparities exist in maternal mortality rates in the U.S. American Indian and Alaska Native women experience mortality rates almost four times higher than white women. Non-Hispanic Black women also face disproportionately high rates of pregnancy-related deaths, underscoring the importance of addressing systemic issues in maternal health care.
What is the significance of postpartum care in reducing maternal mortality?
Postpartum care is critical in reducing maternal mortality, especially because nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year after pregnancy. Enhancing postpartum care can improve recovery and monitoring for complications, ultimately reducing preventable maternal deaths.
Why did the U.S. see an increase in pregnancy-related deaths during the COVID-19 pandemic?
The COVID-19 pandemic may have exacerbated existing disparities and issues within the healthcare system, leading to a sharp increase in pregnancy-related deaths, particularly in 2021. This underscores the pandemic’s impact on maternal health, necessitating targeted interventions in post-pandemic recovery.
What role does healthcare access play in maternal mortality rates?
Access to quality maternal health care is a crucial factor in determining maternal mortality rates. Lack of access can lead to inadequate prenatal and postpartum care, contributing to higher rates of pregnancy-related deaths, particularly among underserved populations.
How can public health infrastructure be improved to address maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Improving public health infrastructure requires increased investment in quality maternal health services, particularly during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Additionally, addressing state-level policy differences and enhancing tracking systems for maternal deaths can help inform effective interventions.
What steps can be taken to address the rising trend of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
To combat rising maternal mortality rates, we must prioritize funding for maternal health initiatives, enhance access to comprehensive care, and implement policy changes that focus on equity in maternal health care across different states and communities.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| U.S. Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, which continued to rise from 2018 to 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, highlighting the need for improved healthcare. |
| Disparities in Mortality | Significant racial disparities exist, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest mortality rates. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The sharpest increase in mortality rates occurred in 2021, influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Leading Causes of Death | Cardiovascular disease now accounts for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths, a shift from previous causes. |
| Investments Needed | There is a critical need for investment in maternal health infrastructure to improve care during pregnancy and postpartum. |
Summary
Maternal mortality in the U.S. is a critical health issue that demands immediate attention and action. The country has recorded the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income nations, with more than 80% of these deaths deemed preventable. Efforts must focus on addressing significant disparities, especially affecting racial minorities, and enhancing healthcare systems, particularly during the postpartum period. With effective investments and policy changes, the tragic trend of rising maternal mortality could be reversed, ensuring healthier pregnancies and better outcomes for mothers across the nation.