Is Sugar Addictive? Understanding Sweet Cravings
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked much debate among nutrition researchers and health professionals alike. While sugar can lead to strong cravings and altered eating behaviors, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria used to classify addictive substances like alcohol or nicotine. Nevertheless, the effects of sugar on the body can be significant, often resulting in withdrawal-like symptoms when consumption is abruptly stopped. Understanding sugar addiction is essential, as high levels of sugar intake can lead to serious health effects, making it vital for individuals to be mindful of their sugar consumption in everyday nutrition.
Exploring the addictive nature of sugar reveals a complex web of interactions between our body and dietary habits. Often referred to as a sweet substance that satisfies our cravings, the effects of this simple carbohydrate can echo those found with harder drugs, leading to a consideration of sugar cravings as a form of dependency. Delving into the realm of sugar addiction, we find discussions about how our diets are saturated with highly processed foods that can amplify our desire for sugary items. Varying opinions abound regarding the health effects of sugar, but modern nutrition research consistently underscores the importance of moderation in our daily sugar intake.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
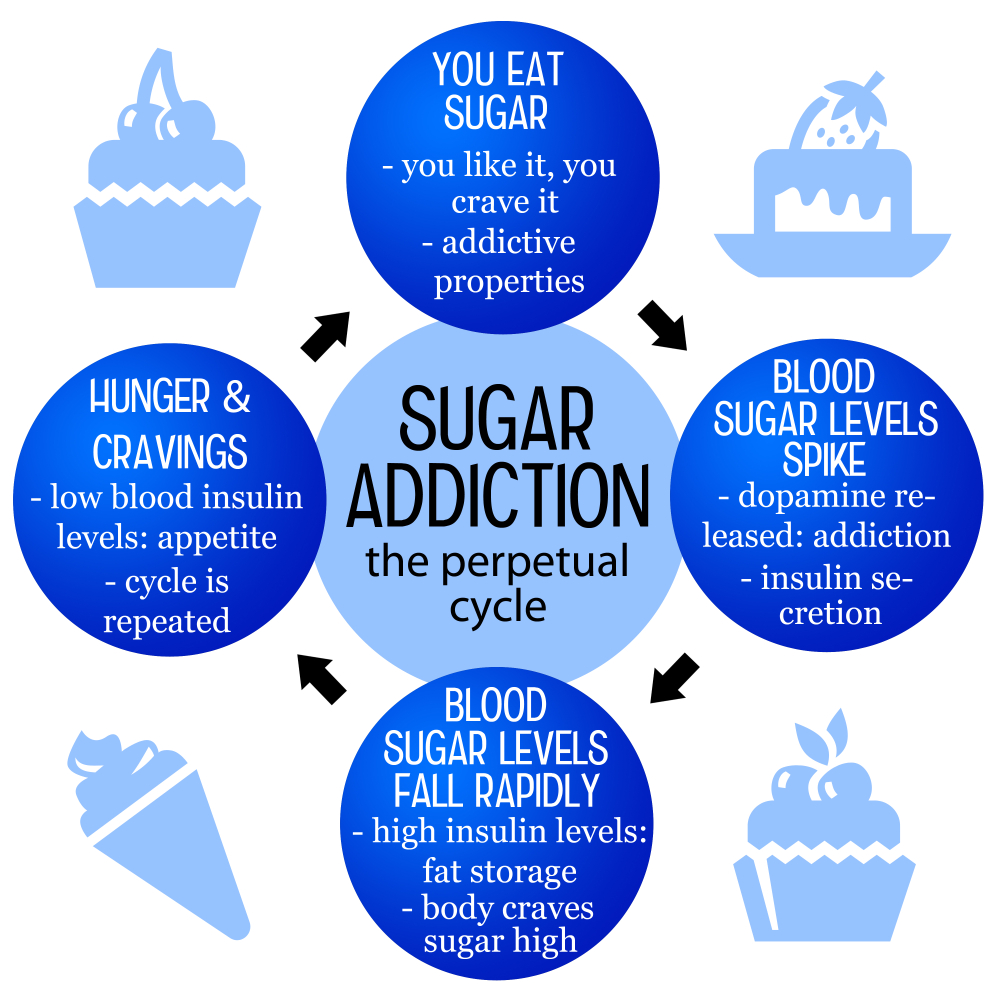
The concept of sugar addiction has sparked considerable debate in the scientific community. While many equate the compulsion to consume sugary foods with the addiction seen in substances like alcohol and nicotine, it is vital to recognize that sugar does not fit neatly into the clinical definition of an addictive substance. Despite not being classified as addictive, sugar affects the brain’s reward pathway much like these substances do, leading to cravings and habitual overeating. This can be particularly troubling given our modern food landscape, which is saturated with ultra-processed items high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium.
Nutrition research indicates that the highly palatable nature of sugary foods increases the likelihood of compulsive eating behaviors. When people attempt to cut sugar from their diet abruptly, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms, such as headaches and anxiety. This suggests a level of dependence on sugar that bears resemblance to addiction. However, unlike drugs or alcohol, sugar is present in many essential foods that contribute to a balanced diet, raising important questions about how society defines and addresses sugar consumption.
The Effects of Sugar on Health
The health effects of sugar consumption are a growing concern in nutrition science. Excessive intake of added sugars is linked with various health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Current recommendations from the American Heart Association advocate limiting added sugar intake to reduce these risks, urging consumers to be mindful of food labels and the hidden sugars in processed foods. On average, Americans consume around 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, which significantly surpasses the recommended limits, warranting attention to dietary habits.
Moreover, sugar consumption impacts not just physical health, but mental well-being as well. Many individuals experience sugar cravings that can lead to mood swings, irritability, and even anxiety. Nutritional studies have demonstrated a correlation between high sugar diets and an increased risk of depression. Recognizing the multispectral effects of sugar on our health can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices that promote overall well-being.
Sugar Cravings: Causes and Solutions
Sugar cravings are multifaceted, influenced by both physiological and psychological factors. Our bodies naturally crave sugar because it provides a quick source of energy and stimulates the release of feel-good chemicals such as dopamine. Yet, the prevalence of sugary snacks and beverages in our environment amplifies these cravings, making it difficult for individuals to consume sugar in moderation. Understanding the underlying causes of these cravings, including emotional triggers and dietary deficiencies, can aid in developing effective strategies for managing them.
To combat sugar cravings, gradual reduction in sugar intake is often recommended rather than going cold turkey. Simple changes, such as swapping sugary snacks for fruits or whole foods, can satisfy sweet tooth cravings while also providing beneficial nutrients. Additionally, incorporating regular meals that stabilize blood sugar levels can minimize the impulsive desire for sugar-laden treats, fostering a more balanced and mindful approach to eating.
Gradual Reduction of Sugar Intake
Adopting a thoughtful approach to reducing sugar consumption can yield significant health benefits. Adults are encouraged to become aware of their daily sugar intake and make concerted efforts to lower it gradually. This might involve substituting high-sugar snacks with healthier options, or being cautious about the sources of added sugars in products. This gradual strategy allows the body to adjust without the shock of sudden withdrawal, which can lead to feelings of deprivation and rob the individual of the joy associated with eating.
In line with the advice from nutrition experts, individuals should aim to replace sugary beverages and snacks with healthier options while still allowing for occasional indulgence. Such moderation not only protects against the potential health effects of sugar but also preserves the psychological aspect of enjoying food. By prioritizing whole foods while remaining mindful of portion sizes, people can develop a more sustainable relationship with sugar that enhances their overall quality of life.
Do We Need Sugar in Our Diet?
Despite ongoing discussions regarding the addictive qualities of sugar, it is important to acknowledge that some sugar is essential in our diets. Natural sugars found in whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy provide not only energy but also vital nutrients that sustain bodily functions. These foods contribute to a balanced diet and offer more than just sugar alone; they come packaged with fiber, vitamins, and minerals that support overall health.
Eliminating all forms of sugar can be impractical and unnecessary. Instead, focusing on minimizing added sugars—those that are processed and added to foods—can lead to better health outcomes. Understanding the differentiation between natural and added sugars is crucial for making informed dietary choices while still enjoying the inherent sweetness that fruits and other wholesome foods provide.
Psychological Effects of Sugar Consumption
Sugar’s psychological impact extends beyond mere cravings; it can also influence mood and mental health. Studies suggest that consuming a diet high in added sugars may increase the risk of mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression. The sugar rush followed by a crash can lead to feelings of irritability and fatigue, which can perpetuate a cycle of craving more sugar to regain that feeling of alertness. Understanding these psychological effects reinforces the need for a balanced approach to sugar consumption, where moderation becomes key to maintaining emotional well-being.
Individuals looking to stabilize their moods may find that reducing their intake of processed sugars results in a more consistent energy level and improved mental clarity. By acknowledging the links between diet and mental health, we can empower ourselves and others to adopt healthier eating behavior, emphasizing whole foods over sugary alternatives. This awareness can lead to significant improvements not just in mental health, but in overall quality of life.
How to Identify Hidden Sugars
Many processed foods contain added sugars that can easily go unnoticed. From sauces and dressings to snacks and beverages, the list of foods laden with hidden sugars is extensive. Being diligent about reading food labels is essential to identify these hidden sources. Nutrition labels provide vital information, including total and added sugars, but sometimes marketing claims can be misleading, making it challenging for consumers to navigate the world of added sugars.
To effectively manage sugar consumption, one should develop skills to decipher labels, seeking products with lower sugar content without compromising on taste or quality. Opting for whole foods and minimally processed options can significantly reduce hidden sugar intake while promoting a healthier diet. In empowering ourselves with knowledge about what to look for, we can make informed dietary choices that encourage a lower sugar lifestyle.
Sugar in Children’s Diets: A Growing Concern
Sugar consumption among children has become an alarming trend, with many kids ingesting far more than the recommended daily allowance. The high prevalence of sugar-sweetened beverages and snacks in children’s diets contributes significantly to health issues like childhood obesity and dental cavities, dramatically affecting their long-term health outlook. Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in limiting their sugar intake by fostering healthy eating habits from an early age.
Educating children about nutrition, including the benefits of enjoying fruits and vegetables over processed snacks, can lay the groundwork for healthier choices in adulthood. Moreover, by modeling balanced eating behaviors and avoiding the normalization of sugar-laden treats, adults can help children form a healthy relationship with food. As awareness of the health effects of sugar continues to grow, parents are encouraged to advocate for healthier food environments at home and in schools.
Curbing Sugar Addiction: Strategies for Success
Successfully managing sugar cravings and possible addiction requires a multifaceted approach. For many, building a support system of friends, family, or health professionals can provide the necessary encouragement and accountability. Strategies such as mindful eating, where individuals focus on the act of eating rather than multitasking, can help in recognizing true hunger cues, ultimately aiding in reducing cravings.
Incorporating physical activity into daily routines also encourages a healthier lifestyle and can diminish urges to consume sugar as a form of comfort or reward. By crafting a personalized action plan that includes balanced meals, exercise, and emotional support, individuals can navigate their relationship with sugar, aiming to reduce its presence in their diets while simultaneously enhancing their overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like drugs or alcohol?
While sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like drugs or alcohol. Research suggests that triggers for sugar cravings often stem from the high palatability of ultra-processed foods rather than true addiction.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
The health effects linked to sugar addiction can include increased weight gain, and risk of type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Although sugar consumption can lead to cravings, its effects are more linked to amounts consumed rather than classified as addiction.
How do sugar cravings impact nutrition?
Sugar cravings can negatively impact nutrition by leading individuals to choose ultra-processed foods high in added sugars, fats, and sodium. This habitual consumption can disrupt balanced eating patterns and overall health.
Can reducing sugar intake alleviate withdrawal symptoms?
Yes, gradually reducing sugar intake can help alleviate withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety. Going cold turkey can exacerbate these effects, so a gradual approach is recommended for managing sugar cravings.
What role does sugar play in our diets?
Sugar, in moderation, contributes to flavor, texture, and pleasure in our diets. It is important to differentiate between necessary sugars found in healthful foods and added sugars that can lead to health issues when consumed excessively.
Are there effective strategies to manage sugar cravings?
Effective strategies to manage sugar cravings include reading food labels for sugar content, opting for whole foods, and gradually reducing sugar intake. These methods can help maintain a balanced diet without feeling deprived.
What is the recommended daily sugar intake?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and even less for children, highlighting the importance of moderation in sugar consumption.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Is Sugar Addictive? | The debate continues, but sugar isn’t classified as an addictive substance like drugs, alcohol, or nicotine. |
| Cravings and Consumption | Sugar does increase cravings but consumption in moderation is key to avoid adverse effects. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Stopping sugar intake can lead to mild withdrawal symptoms like headaches and anxiety. |
| Role in Diet | Sugar is present in many natural foods; its consumption is essential yet should be measured. |
| Average Sugar Intake | Many people consume around 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, exceeding the recommended limits. |
| Conclusion on Addiction | While sugar may have some addictive qualities, it significantly differs from substances that are clinically addictive. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The consensus is that while sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive behaviors similar to addictive substances, it does not meet the clinical criteria for addiction. This nuanced understanding emphasizes the importance of moderation in sugar consumption. Recognizing that sugar holds a vital role in our diets encourages healthier choices and a balanced approach rather than strict dietary restrictions.