TIM-3 Therapy for Alzheimer’s: Revolutionary Research Findings
TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s is emerging as a promising avenue in the quest for effective Alzheimer’s treatment, leveraging insights from cancer therapy. Recent research reveals that by inhibiting the TIM-3 checkpoint molecule, microglia— the brain’s immune cells—can effectively combat amyloid plaques that contribute to cognitive decline. This breakthrough not only suggests a novel approach to tackling Alzheimer’s through immune modulation, but also highlights the critical link between immune system dysfunction and Alzheimer’s disease progression. With the potential to improve memory and cognitive function, TIM-3 therapy represents a significant shift in how we understand Alzheimer’s treatment modalities. As researchers continue to explore this innovative strategy, the hope is to pave the way for therapies that harness the body’s immune response to clear harmful brain debris.
The fight against Alzheimer’s disease has taken a new direction with the exploration of TIM-3 as a therapeutic target. This approach focuses on manipulating immune checkpoint molecules to bolster the brain’s innate defenses against the accumulation of harmful plaques. By enabling microglia, which are the primary immune cells in the brain, to efficiently eliminate these plaques, researchers are uncovering alternative strategies for renormalizing cognitive function. This has drawn parallels to treatments developed for cancer, emphasizing the need for a holistic understanding of the immune system’s role in neurological health. As investigations into the effectiveness of TIM-3 continue, this emerging therapy offers hope for enhancing the quality of life for those affected by Alzheimer’s.
The Potential of TIM-3 Therapy for Alzheimer’s
Emerging research indicates that TIM-3 therapy could revolutionize the treatment landscape for Alzheimer’s disease. TIM-3 is a checkpoint molecule that inhibits the immune response of microglia, the brain’s resident immune cells. By silencing TIM-3’s activity, researchers have observed that microglia are able to engage more effectively with amyloid-beta plaques, which are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s pathology. This proactive engagement allows microglia to clear these toxic aggregates from the brain, potentially reversing cognitive decline and restoring memory functions in affected individuals.
The application of TIM-3 therapy may combine antibodies or small molecules designed to block this checkpoint pathway, thereby allowing microglia to perform their essential function of clearing waste. Clinical trials could pave the way for transforming TIM-3 from a theoretical concept into a practical treatment option. Given the challenges faced in the pharmaceutical development of Alzheimer’s drugs, the focused approach of targeting TIM-3 could yield promising results and offer hope to both patients and caregivers.
Understanding Checkpoint Molecules in Alzheimer’s Treatment
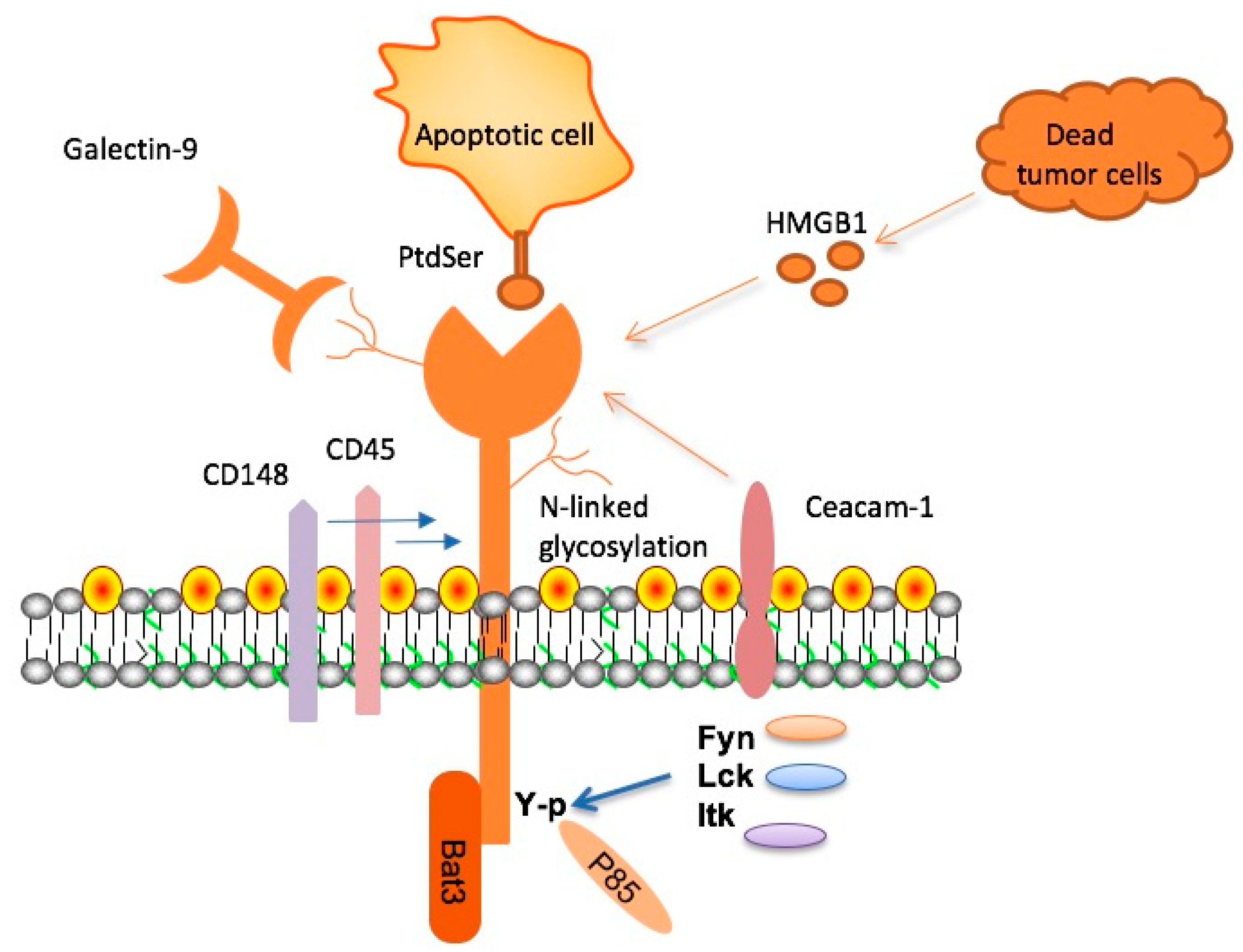
Checkpoint molecules like TIM-3 play a dual role in both cancer and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. In the context of cancer therapy, these molecules are manipulated to weaken the immune system’s capacity to combat tumors, thereby providing a survival advantage to malignant cells. Conversely, in Alzheimer’s, TIM-3 impairs microglia from clearing amyloid plaques—understanding this paradox opens new avenues for therapeutic intervention. By enhancing the ability of microglia to respond to Alzheimer’s pathology, we can potentially reinvigorate the brain’s natural defense mechanisms.
Research has shown that the elevated expression of TIM-3 on microglia in Alzheimer’s patients prevents these cells from performing their waste-clearing duties. As scientists investigate the nuances of these checkpoint molecules, it becomes increasingly clear that novel therapeutic strategies targeting TIM-3 could serve as critical components of comprehensive Alzheimer’s treatment. By facilitating an immune response that enhances cognitive function and memory, such strategies might redefine Alzheimer’s management and effectively slow disease progression.
Microglia: The Brain’s Immune Warriors
Microglia are often described as the brain’s immune cells, responsible for maintaining homeostasis and responding to injury or disease. These specialized cells perform vital functions such as pruning unnecessary synapses during development and clearing debris from the neurological environment. However, in the context of Alzheimer’s disease, their function becomes compromised. The increased expression of inhibitory checkpoint molecules like TIM-3 hampers their ability to clear amyloid plaques that contribute to neurodegeneration.
In healthy circumstances, microglia can effectively manage brain debris and respond to pathological changes, but when their function is inhibited, the accumulation of plaques results in further cognitive decline. Recent studies suggest that employing TIM-3 therapy could help restore the normal functionality of microglia, thereby improving their capacity to clear amyloid plaques. This restoration of microglial activity could be a cornerstone in the development of future Alzheimer’s treatments, highlighting the importance of understanding immune system dynamics in neurological health.
Alzheimer’s Treatment Through Immune System Modulation
The concept of using immune modulation as a strategy for Alzheimer’s treatment is gaining traction in neurobiology. Immune therapies, traditionally associated with cancer treatment, are being re-evaluated in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. This innovative approach seeks to not only slow the progression of Alzheimer’s but also recover lost cognitive functions by harnessing the body’s immune capabilities. As studies uncover the role of immune checkpoint molecules like TIM-3, the potential for a shift in treatment paradigms becomes evident.
By turning the immune system back on, it may be possible to, quite literally, clear the way for neuronal health. Treatments that modulate TIM-3 activity could enhance the brain’s immune responses and optimize the activity of microglia, potentially reversing some of the cognitive impairments associated with Alzheimer’s. Furthermore, this strategy emphasizes the interconnectedness of the immune system and brain health, suggesting that future Alzheimer’s treatments could leverage existing cancer immunotherapies to create new, effective therapies for this devastating disease.
The Role of Genetic Factors in Alzheimer’s and TIM-3
Understanding the genetic underpinnings of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for developing personalized treatments. The TIM-3 gene, HAVCR2, has been linked to late-onset Alzheimer’s, revealing its significance as a genetic risk factor. Studies highlight how certain polymorphisms in this gene significantly increase TIM-3 expression on microglia, affecting their ability to clear amyloid plaques. This genetic correlation suggests that therapies targeting TIM-3 could be particularly effective in individuals with specific genetic predispositions.
As researchers delve into the genetics of Alzheimer’s, the importance of such markers in the treatment paradigm becomes clearer. Identifying individuals at risk due to genetic factors allows for earlier and more targeted intervention strategies. In establishing TIM-3 as both a therapeutic target and a genetic marker, there’s potential to create customized treatment plans that take into account the unique genetic profiles of patients, making TIM-3 therapy a cornerstone in the future of precision medicine for Alzheimer’s disease.
Navigating Alzheimer’s Cognitive Testing in Research
Research into TIM-3 therapy also includes innovative approaches to evaluate its effectiveness through cognitive testing in mouse models. Researchers measure cognitive behaviors by assessing memory capabilities, such as the ability to navigate mazes. These methodologies provide invaluable insights into the therapeutic impact of TIM-3 modulation—indicating that if memory functions improve in these models, there may be a tangible benefit for human patients suffering from Alzheimer’s.
The importance of cognitive testing extends beyond simple memory tasks; it assesses a range of behaviors linked to anxiety, navigation, and social interaction. Lessons learned from these testing protocols inform how future human clinical trials might be structured, ensuring the identification of meaningful improvements in cognitive function. As researchers continue to refine their methodologies, the interplay between TIM-3 modulation and cognitive assessments will solidify the foundation for emerging Alzheimer’s therapies.
Challenges in Alzheimer’s Drug Development
The journey toward effective Alzheimer’s treatments has been fraught with challenges, with many drug trials ending in failure despite promising initial results. A significant barrier has been the complex nature of amyloid pathology, as anti-amyloid therapies have often encountered limitations related to penetration into the brain and vascular safety. Consequently, the repurposing of TIM-3 antibodies presents a novel strategy that could bypass these traditional hurdles while enhancing the immune response.
An innovative approach utilizing TIM-3 inhibitors may enhance the effectiveness of existing therapies and create new pathways for drug development. By addressing the immune system’s role in plaque clearance, researchers could redefine therapeutic efficacy in Alzheimer’s studies. Building upon the lessons learned from both successes and failures in drug development can guide future research efforts toward viable treatments that genuinely impact patient outcomes.
Collaborative Efforts in Alzheimer’s Research
Alzheimer’s research, particularly in the realm of TIM-3 therapy, relies heavily on collaborative efforts within the scientific community. Research teams, such as the collaboration between Dr. Vijay Kuchroo and Dr. Oleg Butovsky, demonstrate the power of interdisciplinary approaches. By combining expertise across immunology and neurology, these teams work to discover new insights into the immune system’s role in Alzheimer’s pathology and treatment.
Such collaborations enable the pooling of resources, ideas, and techniques, accelerating the pace of discovery. As researchers share findings and methodologies, the potential for breakthroughs increases, particularly in areas as complex as Alzheimer’s disease. Multifaceted approaches, including cooperation with human clinical trials, are essential for translating preclinical findings into clinical solutions that can effectively combat Alzheimer’s and improve quality of life for those affected.
Future Directions for TIM-3 Research in Alzheimer’s
With initial studies indicating the potential of TIM-3 therapy in Alzheimer’s treatment, the future looks promising yet challenging. Ongoing research aims to explore the effectiveness of human anti-TIM-3 antibodies in preventing plaque development in mouse models. Successfully integrating these findings into human trials could signify a substantial leap forward in managing Alzheimer’s disease.
Furthermore, as scientists refine their understanding of TIM-3’s roles and its manipulation, future inquiries could expand into combination therapies that address not only amyloid plaques but also tau pathology and neuroinflammation. As the breadth of research continues to evolve, TIM-3 therapy could potentially unlock new avenues for therapeutic interventions to mitigate Alzheimer’s symptoms and improve patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s and how does it work?
TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s involves blocking the TIM-3 checkpoint molecule, which inhibits microglial immune cells from clearing amyloid plaques in the brain. By deleting or inhibiting TIM-3, these immune cells can effectively attack and clear the harmful plaques, potentially improving cognition and memory in Alzheimer’s patients.
How does TIM-3 relate to immune system responses in Alzheimer’s treatment?
In Alzheimer’s treatment, TIM-3 acts as a stop signal for microglia, the brain’s immune cells, which prevents them from attacking amyloid plaques. Targeting TIM-3 may help revitalize these immune responses, thus enabling the clearance of plaques associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
What are the potential benefits of TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s patients?
TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s might enhance the ability of microglia to remove toxic amyloid beta plaques, thereby restoring cognitive function. Preliminary studies in mice have shown improved memory and cognitive behavior following TIM-3 inhibition.
Can TIM-3 therapy be used alongside other Alzheimer’s treatments?
Yes, TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s could potentially be combined with other treatments. Its specific mechanism of action targeting immune responses complements existing anti-amyloid therapies, which could enhance overall treatment outcomes.
What findings support the use of TIM-3 therapy in Alzheimer’s research?
Research published in Nature demonstrated that deleting TIM-3 in mice led to enhanced clearance of Alzheimer’s-related plaques and improved cognitive performance. This suggests a promising avenue for developing TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s patients.
Are there existing therapies that target TIM-3 for Alzheimer’s treatment?
Currently, therapy targeting TIM-3 is still in research phases, but existing anti-TIM-3 antibodies, used in cancer treatment, have potential for repurposing in Alzheimer’s treatment as they selectively target the immune response.
What challenges are associated with developing TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s?
Challenges include ensuring the therapeutic agents effectively reach the brain due to the blood-brain barrier and determining optimal dosing and administration methods to maximize clearance of amyloid plaques without adverse effects.
How long has research into TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s been ongoing?
Research into TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s has been ongoing for about five years. This includes extensive studies to understand the role of TIM-3 in the immune response related to Alzheimer’s pathogenesis.
What is the next step for TIM-3 therapy research in Alzheimer’s?
The next step involves testing human anti-TIM-3 antibodies in Alzheimer’s mouse models to assess their efficacy in halting the development of brain plaques and improving cognitive functions associated with Alzheimer’s.
How prevalent is the TIM-3 gene polymorphism in Alzheimer’s patients?
The TIM-3 gene polymorphism is identified as a genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, found in a significant proportion of Alzheimer’s patients, contributing to altered immune responses in the disease.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| TIM-3 Molecule | TIM-3 is a checkpoint molecule that inhibits immune activity in the brain, particularly in microglia, the brain’s immune cells. Its inhibitory action prevents microglia from clearing amyloid plaques associated with Alzheimer’s disease. |
| Role in Alzheimer’s | TIM-3 has been linked to late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (90-95% of cases) and is a genetic risk factor that impedes the clearance of amyloid plaques. |
| Research Findings | Deleting the TIM-3 gene in mice leads to enhanced plaque clearance by microglia, resulting in improved cognitive functions. |
| Potential Therapy | Therapeutic strategies could involve using anti-TIM-3 antibodies or small molecules to enhance microglia’s ability to clear plaques in Alzheimer’s patients. |
| Future Research | Ongoing studies aim to test human anti-TIM-3 antibodies in mouse models to assess their ability to reduce plaque development. |
Summary
TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s presents a promising avenue for treatment by addressing plaque accumulation in the brain. The study led by Vijay Kuchroo at Harvard Medical School reveals that manipulating TIM-3 can free microglia to effectively clear amyloid plaques, potentially improving cognitive function. This unexpected linkage between cancer treatment strategies and neurodegenerative diseases opens new pathways for therapeutic interventions against Alzheimer’s, highlighting the significance of the immune system in brain health.